Health
5 Benefits of macrobiotic diet and side effects

Discover the 5 shocking health benefits of a macrobiotic diet and side effects.
The meaning of the macrobiotic diet is “great life.” As stated by the Kushi Institute – one of the world’s leading authorities on the macrobiotic diet
«This is not simply a diet, macrobiotics recognizes the profound effects that food, the environment, activities and attitudes have on our body- mind-emotions ».
The core concepts of the macrobiotic diet, including the Traditional Chinese Medicine belief that it balances yin and yang in both the body and the environment, date back many centuries in ancient Eastern traditions.
Proponents of macrobiotic eating approaches have long encouraged people to eat natural, whole foods that not only support the health of their bodies, but also the ecosystem and natural order of life.
As a “countercultural” approach to eating, macrobiotic diets became fashionable in the United States during the 1960s because they encouraged living in harmony, practicing a positive mindset, and viewing food as much more than just calories or fuel. .
Although each person reacts differently to different dietary approaches, evidence shows that macrobiotic-style diets can help improve heart health, reduce inflammation, and support a healthy body weight well into old age.
What is the macrobiotic diet
The macrobiotic diet is a plant-based diet rooted in yin-yang theory that comes from Asia.
According to macrobiotic theory, the balance between yin and yang is achieved through a mainly vegetarian diet, low in fat, with a balance of different macronutrients (proteins, carbohydrates and fats), foods that have different energy qualities and a wide range of vitamins and minerals from plants.
This approach to eating is believed to better support agriculture, local farming, digestion, and even mental well-being.
Other recommendations for eating a macrobiotic include buying locally grown produce, buying organic foods that are not treated with chemical pesticides, consuming foods in season, consuming mostly fresh and raw foods, and an emphasis on organic foods. plant foods over meat, dairy and other animal products.
Most macrobiotic diets emphasize the consumption of a wide variety of plant foods, which means that these diets tend to be relatively high in carbohydrates.
However, because refined sugar and processed/ packaged foods are not part of the macrobiotic plan, these carbohydrates are “complex,” great sources of dietary fiber, and packed with antioxidants and other nutrients.
Although there are many different varieties of macrobiotic diets that are consumed around the world, most have roughly the following breakdown:
• More than 50 percent of calories come from complex carbohydrates (sometimes even up to 80 percent), 15 to 30 percent from healthy fats, and 10 to 20 percent from protein.
Although carbohydrates are consumed in large quantities, refined carbohydrates such as processed grains and sugar are avoided.
• A high proportion of the carbohydrates in macrobiotic diets (about 25 to 30 percent of total calories) comes from fresh or cooked vegetables.
This is a very high percentage considering how low in calories vegetables naturally are.
• Complex carbohydrates, such as brown rice, barley, millet, oats, and organic (non-GMO) corn are also commonly consumed, accounting for 30 to 40 percent of total calories.
• Many also get 5 to 10 percent of their calories from legumes or beans, often the fermented types like tempeh, miso, or tofu.
• Sea vegetables are a staple in most macrobiotic diets, accounting for 5 to 10 percent of total calories.
• A small percentage, about 5 percent of calories, tend to come from fish or shellfish (usually eaten several
times a week on average).You may notice that macrobiotic diets have a lot in common with the famous Okinawan Diet, which is not surprising considering that both have similar roots in Asian cultures.
The Okinawan Diet is named after the largest island of the Ryukyu Islands in Japan and is consumed by some of the healthiest and longest-lived people in the world.
In fact, Okinawa has been coined as one of the Blue Zones of the world, where people have the highest chance of living in the last 100 years.
The average life expectancy in the United States is 78.8 years, but it is between 80-87 years in Japan (higher for women than for
5 benefits of a macrobiotic diet
Below are the 5 benefits of a macrobiotic diet for health:
1.- Benefits of macrobiotic diet for inflammation
• In 2015, the University of Memphis School of Public Health published the findings of a study investigating the anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer potential of macrobiotic diets.
The study compared the nutrient composition of a macrobiotic diet plan with the National Dietary Recommendations (CDR) based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES).
• A key comparison was evaluating which approach scored high on the Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII), as well as comparing levels of total calories, macronutrients, and 28 micronutrients.
• The results showed that the macrobiotic diet plan had a lower percentage of energy from fat, a higher intake of dietary fiber, and higher amounts of most micronutrients.
Nutrients in the macrobiotic diet often met or exceeded the RDA recommendations, with the exception of vitamin D, vitamin B12, and calcium.
• Based on DII scores, the macrobiotic diet was found to be “more anti-inflammatory compared to NHANES data,” and the researchers concluded that the overall findings indicated potential for disease prevention when a macrobiotic eating approach was followed.
2.- Benefits of macrobiotic diet for heart
• Certain studies have found evidence of macrobiotic-style diets that support cardiovascular health, particularly lowering serum lipid levels and lowering blood pressure levels.
This is not surprising considering how many high antioxidant anti-inflammatory foods are encouraged in a macrobiotic diet.
For example, the macrobiotic diet is rich in dietary fiber, including all kinds of fiber-rich foods, such as raw vegetables, beans, and ancient grains.
• Eating plenty of fiber has been correlated with improvements in cardiovascular disease risk factors through multiple mechanisms, including lowering lipids, regulating body weight, improving glucose metabolism, controlling blood pressure, and blood pressure. reduction of chronic inflammation.
3.- It can help maintain a healthy weight
• Like those who eat the Okinawan way, proponents of the macrobiotic diet focus not only on eating the right foods, but also eating them in the correct amounts.
• The macrobiotic diet emphasizes eating carefully, slowing down and savoring meals, paying attention to physical sensations (also called biofeedback), and chewing food thoroughly.
• This approach can help you better control how much you eat, give you more pleasure from having less, teach you to avoid emotional eating out of boredom or other negative feelings, and achieve satiety more easily.
• Rather than trying to lose weight simply by cutting out too much food or consuming less, which can lead you to feel overly hungry and deprived, eating mindfully and choosing foods wisely can help you feel more in touch with your body’s needs.
4.- Very Low in Sugar, Gluten and Packaged Foods
• Like other whole-food-based diets that eliminate junk foods, packaged goods, bottled drinks, fried foods, and fast foods, the macrobiotic diet is very low in sugar, empty calories, and artificial ingredients.
• This makes for a very nutrient-dense diet, high in things like vitamin C, vitamin E, and fiber, but generally low in calories.
• It can also be potentially beneficial for food allergy sufferers as it removes common allergens that can cause indigestion, such as dairy products, almost all gluten, and acorns.
• However, a drawback and point of criticism is that macrobiotic diets tend to include a lot of salty and high-sodium foods, mainly from things like soy sauce, fermented soy products, and sea vegetables.
5.- Benefits of macrobiotic diet for cancer
• Although diet is only one piece of the total puzzle when it comes to preventing cancer, and results vary from person to person, research suggests that consuming a macrobiotic diet may help reduce cancer risk in part by providing high levels of antioxidants and phytoestrogens.
• A 2011 report published in the Journal of Nutrition stated, “Based on the available evidence and its similarity to dietary recommendations for chronic disease prevention, the macrobiotic diet probably carries a reduced risk of cancer.”
• Women who consume macrobiotic diets tend to have modestly lower circulating estrogen levels, which has been linked to a lower risk of breast cancer.
• Macrobiotic diets provide high amounts of phytoestrogens from foods like fermented soy products and sesame seeds , and these can help regulate natural estrogen production by binding to estrogen receptor sites.
• While too much estrogen comes with its own risks, for women over 50 who naturally experience decreased levels during menopause, the extra estrogen from their diets could help lower their risk of cancer, among other benefits.
How to Consume Macrobiotic Diet
Foods that are considered macrobiotics include:
• All types of fresh vegetables other than night shade, especially daikon radishes, cooked or fresh leafy greens such as bok choy, cabbage, mushrooms, chives, leeks, broccoli, carrots, beets, various varieties of squash, watercress, and cauliflower.
• Fresh herbs, including ginger, garlic, coriander, etc., plus soy sauce, tamari, fish sauce, brown rice syrup, and honey for sweetening or flavoring.
• Algae and seaweed
• Beans and legumes, tofu, tempeh, adzuki beans, black beans, and edamame
• Nuts and seeds, including sesame, pumpkin, almonds, and cashews
• Raw old grains – this includes all types of rice (especially brown rice), millet, barley, buckwheat, amaranth, quinoa, rye, oats, and organically grown corn.
• Noodles made from brown rice, soba, and other grains
• Miso or fermented soy seasonings (and miso soup)
• Unrefined oils made from things like sesame or pumpkin seeds
• Tea, such as green, black, jasmine, white, long oo, bancha, dandelion, grass, etc.
Foods to avoid on a macrobiotic diet:
• Packaged and processed foods
• Dairy products
• Meat
• Eggs
• Refined sugar and sweeteners
• Chocolate or cocoa products
• Most fruits, especially tropical ones
• Coffee
• Strong or hot spices
•Night-shade vegetables: This includes avoiding dark-colored vegetables, such as eggplants, tomatoes, potatoes, and bell peppers. How is that, you may be wondering?
Although belladillas are not a problem for a high percentage of people, some experience digestive symptoms when consuming these foods, including allergies, symptoms of intestinal leakage and autoimmune reactions.
However, eliminating these vegetables in general is a common criticism of the macrobiotic diet as many feel this is not necessary for most healthy people.
Macrobiotic diet plan and lifestyle tips
• Cook fresh food at home more often, especially on a gas stove, which reduces the amount of leftovers and microwave, frozen, or canned food you eat.
• Make plants the center of your meals by only consuming fresh and wild seafood (and especially meat or dairy) in limited quantities.
• Try to eat a variety of colored fruits and vegetables every day, as different colors indicate different antioxidants.
• Drink plenty of clean water and tea, avoiding sweetened beverages, alcohol, and caffeine.
• Try to chew your food well to improve digestion and also slow down during meals. The ideal is to chew up to 25-50 times according to the macrobiotic diet theory.
• Use glass to store food and water instead of plastic products.
• The Great Life Global organization also recommends other macrobiotic lifestyle tips to improve balance, such as opening windows every day for fresh air, keeping plants indoors, walking outside, sticking to a regular sleep schedule.
And wakefulness, practicing gratitude daily, learning to cook at home more often, wearing clothing made from natural fibers, exfoliating with hot towels, or brushing your skin to detoxify and chew your food thoroughly while eating.
Recipes for a macrobiotic diet
•For breakfast: a green smoothie, brown rice porridge with nuts and seeds, or a tasty and traditional breakfast of miso soup, vegetables and legumes.
•For lunch: miso soup with seaweed, a small amount of wild fish, sautéed vegetables, and a serving of unprocessed grains, such as brown rice. The tea can also be consumed throughout the day.
•For dinner: Similar to lunch, such as soup with soba noodles and vegetables, fermented beans or tempeh for protein with seaweed salad, or a stir fry made with vegetables, grains, nuts and seeds.
Macrobiotic diet vs. Paleo diet
• The Paleo diet is modeled after what our ancestors are believed to have eaten thousands of years ago – that is, only natural foods that could have been found within their local environments.
• Because both the macrobiotic diet and the paleo diet emphasize the consumption of organic, unprocessed, local and seasonal foods, the two diets have some underlying principles in common – however, certain foods also differ between the two approaches.
• One of the biggest differences between macrobiotic diets and paleo diets is that macrobiotic diets are plant-based, sometimes even completely vegetarian / vegan.
People who eat a macrobiotic diet get their protein from plant-based foods like tofu, legumes, beans, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and occasionally some shellfish.
• The paleo diet tends to include more animal protein, including meat, fish, eggs, and poultry.
However, both approaches avoid dairy products and all processed vegetarian proteins (such as soy isolate or synthetic protein powders).
• The paleo diet also eliminates all beans, legumes, and grains for the most part, while the macrobiotic diet encourages these foods.
However, both diets reduce or eliminate added sugar, synthetic additives, artificial ingredients, refined oils, fried foods, and sometimes common allergens like belladonna greens and gluten.
Side effects of macrobiotic diet
Although the macrobiotic diet is considered one of the most popular alternative or complementary dietary approaches for the treatment of chronic diseases, including cancer, few studies have been able to really demonstrate its effectiveness in preventing or treating disease.
Therefore, more research is still needed before drawing conclusions about the healing benefits of this diet.
According to some experts, there are concerns regarding treating cancer with dietary approaches, such as macrobiotics, including:
• Patients who potentially delay conventional treatments and doctor visits
• Possibly developing nutritional deficiencies that impair immune function, such as consuming too little vitamin D, calcium, and protein
• Eating too few calories overall, which can cause muscle loss and fatigue – this can be made worse by low levels of iron and vitamin B.
• Some also find that macrobiotic diets have social limitations (due to strict adherence to this diet) that make them difficult to follow.
Additionally, macrobiotic ingredients can be difficult to obtain, and the salt intake in this diet plan is considered too high by some.
There is also disagreement on the need to eliminate most fruits, including all tropical fruits.
These are all valid arguments and should be weighed against your personal preferences, beliefs, and your overall health.
If you have an existing condition, such as heart disease or cancer, or if you take medication, it is a good idea to get a professional opinion if you start a new way of eating and experience any negative signs or symptoms.
Final thoughts
• A macrobiotic diet is a dietary approach that comes from Asian traditions that emphasize the consumption of mainly vegetable (vegetarian) proteins, low amounts of animal foods and fats, and a balance of different micro and macronutrients that support the energy balance of yin -yang in the body.
• Macrobiotics argue that foods that have different energy qualities and a primarily plant-based diet are good for health (especially the digestive system) and also good for the ecosystem.
• An emphasis on local, seasonal and fresh plant-based foods is believed to support agriculture, local farming, and mental well-being. It could also support heart health, promote longevity, and offer protection against cancer.
• Important practices when consuming macrobiotic foods include buying locally grown organic products, cooking often at home, avoiding packaged foods, eating fermented and raw foods, and limiting dairy and animal products.
• Although a macrobiotic diet has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, some concerns are that macrobiotic diets are high in salt but relatively low in protein, fruit antioxidants, vitamin D, calcium, and sometimes B vitamins.
We hope the article on the 5 benefits of a macrobiotic diet for health has been of help.
Health
15 good reasons to drink lemon juice in the morning on an empty stomach
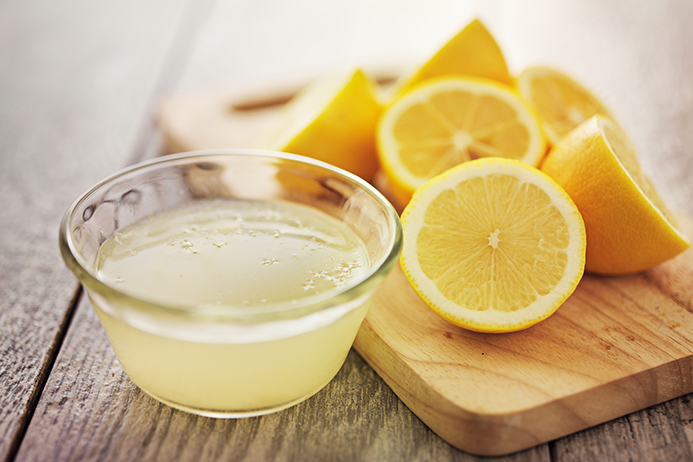

Discover the 15 good reasons to drink lemon juice in the morning on an empty stomach.
Lemon is one of the most frequently and widely used citrus fruits.
Its popularity is due to its scent and refreshing taste.
Its aroma makes it an ingredient of choice in many recipes and the composition of perfumes.
It also accompanies a large number of drinks, including tea and cocktails, it can also be served as fruit juice.
Not only is lemon used for its aromatic qualities, but also its therapeutic dimension.
Rich in vitamin C, lemon indeed has formidable therapeutic virtues: its Antiviral and antibacterial properties as well as its ability to stimulate the immune system are widely recognized.
One of the most common ways to reap the benefits of lemon is by squeezing the juice.
Lemon juice stimulates digestion and has a detoxifying action.
It also promotes drainage of the liver and thus improves digestion.
By its ability to boost metabolism, lemon juice is an effective way to lose weight.
If you want to lose weight, drinking lemon juice in lukewarm water every morning on an empty stomach gives fabulous results.
But that’s not all, nutrition specialists at the Edison Institute of Nutrition have compiled a list of the main benefits of consuming lemon juice mixed with lukewarm water on an empty stomach:
1. An excellent source of vitamin C, lemon juice protects the body by strengthening the immune system.
2. Drinking lemon juice in lukewarm water every morning on an empty stomach helps maintain pH balance in the body.
3. Thanks to its antibacterial properties, lemon juice helps fight infections.
4. Has a detoxifying action.
5. Promotes digestion.
6. Besides vitamin C, lemon is also an excellent source of potassium, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, etc.
7. Helps fight colds.
8. Lemon water is a well-known remedy for dealing with different skin problems like acne, rashes, wrinkles, or dark spots.
9. Mixed with lukewarm water, lemon juice stimulates digestion, boosts metabolism, and thus allows you to lose weight quickly.
10 Lemon juice is also very effective in removing toxins that have accumulated in the liver.
11. The anti-inflammatory properties of lemon help fight infections of the respiratory tract, sore throat, and inflammation of the tonsils.
12. Rich in electrolytes, lemon juice effectively hydrates the body.
13. Drinking lemon juice mixed with lukewarm water decreases muscle and joint pain.
14. Lemon juice in lukewarm water promotes good dental hygiene because it helps decrease dental pain and prevent gingivitis.
15. Drinking lemon juice in lukewarm water stimulates digestion and regulates intestinal transit.
SOME QUESTIONS / ANSWERS AND COMMENTS :
Q. Out of curiosity… my cousin is allergic to lemon. Does lime have the same virtues?
A. Yes, you can substitute lemon for lime.
I had to stop drinking lemon water for a month because I was sick. The joint pain I got rid of before all came back.
So I started drinking lemon juice in lukewarm water again every morning on an empty stomach.
Now after a week, and it’s true, my pain in my knees is gone !!!!
It’s amazing! Lemon is indeed very alkalizing and promotes the elimination of acids.
Also, it contains a lot of vitamin C, which is good for the joints.
Some people suffer from vitamin C deficiency and need to be sure to find it in their diet or supplements.
Q. After drinking lemon juice in lukewarm water in the morning on an empty stomach, how long should I wait to eat?
A. I recommend that you wait 20 to 30 minutes before eating.
Q. Why does lemon juice need to be mixed with lukewarm water? Is lemon juice also beneficial in cold water?
A. Lukewarm water stimulates digestion and the liver.
Coldwater does the opposite, it blocks digestion.
So it is best to consume lemon juice in lukewarm water.
Q. How many lemons should you squeeze in the morning to benefit from the benefits of this fruit?
A. I suggest squeezing half a lemon in a large glass of lukewarm water (25cl).
Lemon juice is rich in vitamin C and antioxidants.
Citric acid and vitamin C promote the dissolution of gallstones, their elimination, as well as the clearing of the bile ducts.
Lemon juice has been used for centuries in the treatment of kidney stones and gallstones.
Lemon also has antimicrobial properties that help reduce gallbladder infections and relieve pain.
The pectin in lemon juice relieves bloating, nausea and pain.
Besides, lemon juice helps reduce the production of cholesterol by the liver.
Q. Hello. I have a question: I have thyroid problems, can I drink lemon juice in lukewarm water?
A. Yes. You can drink lemon juice in lukewarm water if you are suffering from thyroid problems.
Q. I take medicine on an empty stomach every morning for a thyroid problem. Should I take this medicine before drinking lemon water or after?
A. Since lemon water is absorbed relatively quickly by the body, I recommend that you take your medicine soon after drinking the lemon water.
Joint pain is associated with poor digestion and allergic reactions to certain foods.
Lemon water promotes digestion and the elimination of toxins.
If your teeth are prone to demineralization and are very sensitive, I advise you to drink lemon water through a straw.
Health
Mosquito bite: The Miracle Cure Against It
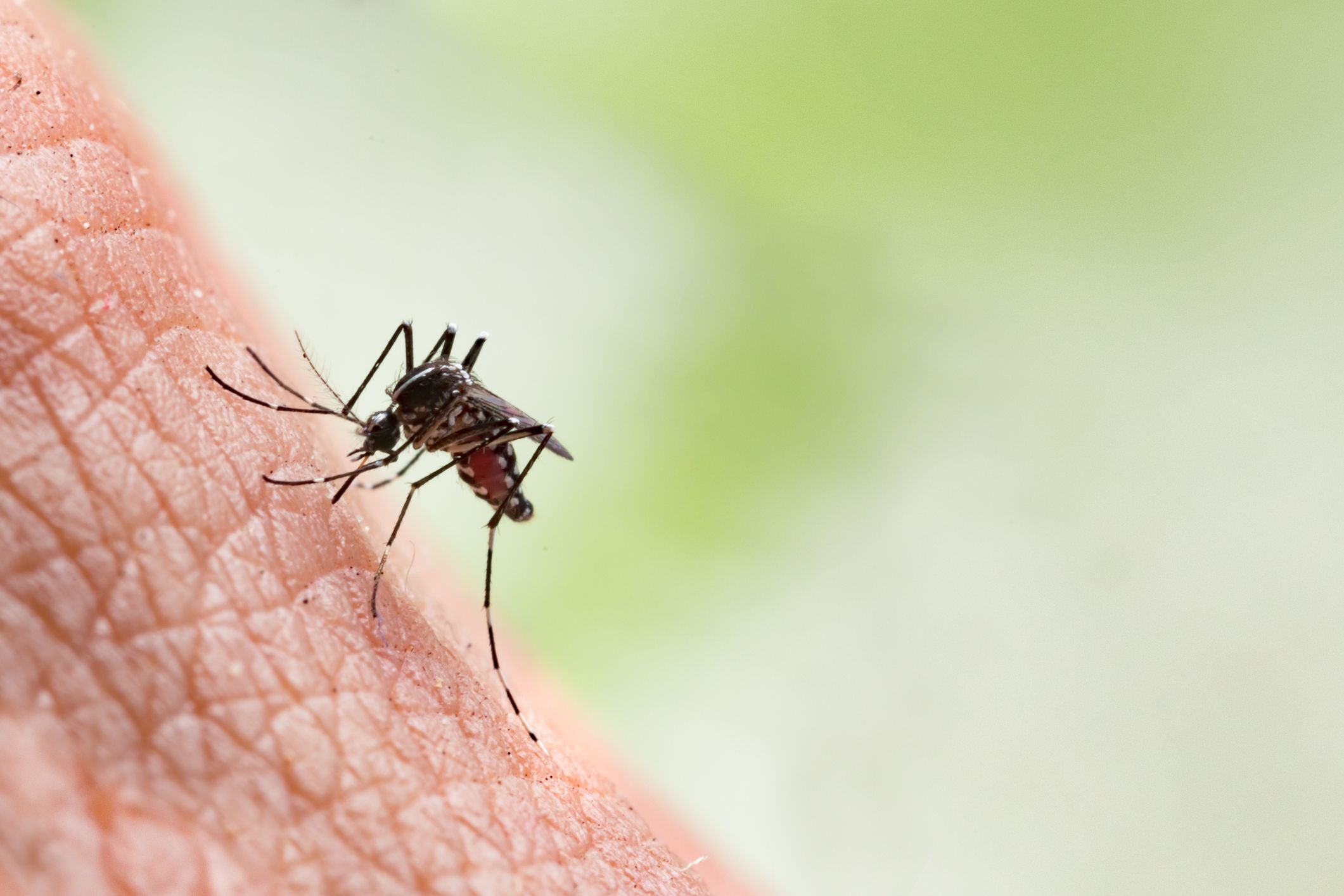
Discover The Miracle Cure Against Mosquito Bite.
Have you been bitten by a mosquito again?
They have the gift of stinging us when we spend a quiet evening on the terrace!
And then, hello the itching!
We only want one thing, and that is to scratch ourselves to the point of blood. It’s super annoying!
Fortunately, my grandmother gave me her natural remedy to quickly relieve a mosquito bite.
The miracle trick is to apply a paste of baking soda and witch hazel water. Look :
What you need
- baking soda
- witch hazel water
- cup
How to do
- Put three teaspoons of baking soda in a cup.
- Pour a teaspoon of witch hazel water
- Mix to obtain a paste.
- Apply the paste to the bite.
- Leave on.
Results
And there you have it, thanks to this remedy, you have stopped the itching of mosquito bites in their tracks 🙂
Easy, fast, and efficient, isn’t it?
It is a simple treatment that makes the sting deflate and disappear quickly!
This remedy is completely natural and very gentle. It is ideal for the fragile skin of children and babies.
And you don’t even need Apaisyl cream … it’s much more economical that way.
In addition, it works for all insect bites: mosquitoes, spiders, horseflies…
Why does it work?
Baking soda soothes the itchiness. It acts as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It thus calms the inflammation caused by the sting.
Witch hazel water also disinfects the sting and soothes the itchy sensation.
It also refreshes the skin and heals the irritated part thus bringing an immediate feeling of well-being.
We also find witch hazel in the composition of calming gels after insect bites from Hansaplast.
What is witch hazel?
Witch hazel is a plant native to North America.
Witch hazel water comes from the indirect distillation of dried witch hazel leaves. It takes about 60 kilos of leaves to get a thousand liters of water.
The many benefits of witch hazel have been recognized for a very long time.
It helps disinfect wounds. Applied in massage, it is an effective venous tonic and stimulates blood circulation.
It also has anti-inflammatory properties and as such, it relieves rheumatic and arthritis pain.
It is also an asset in your beauty kit. Used in rinsing water, it eliminates dandruff.
Finally, it is also found in perfumery, because its smell is very pleasant. It is similar to that of cut grass with a hint of mint in addition.
Health
17 Benefits of Garden Cress You Never Dreamed of

Table of Contents
-

 Benefits5 months ago
Benefits5 months agoThe Benefits of Joining Gym Lumolog – Improve Your Fitness & Health
-

 Food1 year ago
Food1 year ago10 + Benefits of carrot juice and side effects
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year ago50 Super Healthy (And Very Often Cheap) Foods
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year ago5 Shocking health benefits of kinkeliba and side effects
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year ago15 health benefits of soursop leaves tea and side effects
-

 Food1 year ago
Food1 year ago8 shocking benefits of leek juice and side effects
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year ago15 Benefits of lipton tea and side effects
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year agoBenefits of guava leaves Sensually












