Health
22 Benefits of turmeric milk and side effects
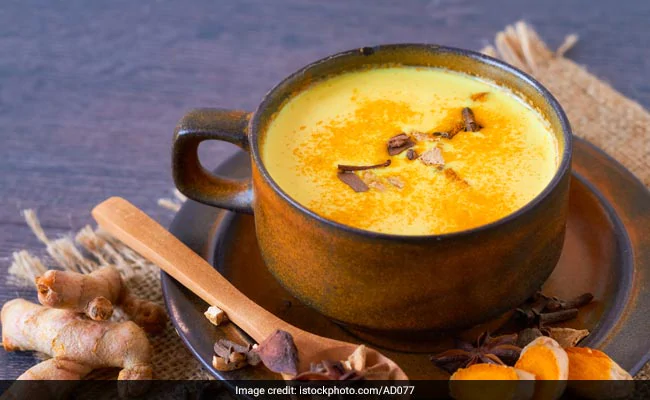

Discover the 22 shocking health benefits of turmeric milk or golden milk and side effects.
Turmeric is a popular spice around the world, but turmeric milk is a valuable and potentially beneficial drink that many people don’t even know about.
Packed with nutrients and capable of affecting health in many different ways, it is important to understand all that this popular drink can do.
What is turmeric milk?
Turmeric milk, as the name implies, is an infusion composed of dried turmeric root or turmeric powder mixed with milk to create a delicious golden drink.
In fact, this traditional tonic from India is often referred to as ‘golden milk’.
While the taste is slightly bitter, milk tends to remove most of the spiciness from turmeric.
This drink is also formally known as Haldi Ka Doodh , and is usually made with just turmeric and milk.
It can include powdered cardamom, ground ginger, pepper, or cloves, making the drink even more beneficial to your health.
There are not enough fingers to list its benefits, because turmeric, in addition to being one of the oldest spices, can improve our quality of life
Benefiting from the antioxidants and active ingredients in turmeric, as well as the mineral components of milk, this is one of the best beverages to use as a general tonic for the body.
Health benefits of turmeric milk
The most notable benefits of turmeric milk include improving skin health, alleviating digestive problems, preventing cancer, promoting weight loss, and protecting the respiratory system, among others.
Here are the best health benefits of turmeric milk:
1. Respiratory disease:
Turmeric milk is antimicrobial and fights bacterial and viral infections.
It is useful in the treatment of diseases related to the respiratory system, as the spice warms the body and provides rapid relief from lung and sinus congestion.
This is also an effective remedy to cure asthma and bronchitis.
2. Benefits of turmeric milk for cancer
This milk made from raw turmeric prevents and stops the growth of breast, skin, lung, prostate and colon cancers, as it has anti-inflammatory properties.
This prevents cancer cells from damaging DNA and reduces the side effects of chemotherapy.
3. Anti-inflammatory:
Turmeric milk is anti-inflammatory and can prevent and protect arthritis and stomach ulcers.
It is also known as a natural aspirin in Ayurvedic medicine and can cure headaches, swelling, and pain.
4. Benefits of turmeric milk for cough
Turmeric milk is considered the best cold and cough remedy due to its antiviral and antibacterial properties.
Gives instant relief from a sore throat, cough and cold.
In fact, you can fight that bad cold if you start drinking turmeric milk every day.
5. Golden Milk For Joints
Turmeric milk is used to cure arthritis and treat swelling due to rheumatoid arthritis.
It also helps make your joints and muscles more flexible by reducing pain.
6. May relieve pain
Golden turmeric milk provides the best relief for aches and pains, especially back pain.
This can also strengthen the spine and joints in the body.
7. A powerful antioxidant
Hot milk with turmeric powder is an excellent source of antioxidants that fight free radicals. It can cure many ailments.
8. Blood purifier
Turmeric milk is considered an excellent blood purifier and cleanser in Ayurvedic tradition.
It can revitalize and increase blood circulation in the body.
It is also an anticoagulant that cleanses the lymphatic system and blood vessels of all impurities.
9. Benefits of turmeric milk for liver
Turmeric milk is a natural liver detoxifier and blood purifier that increases liver function.
It supports the liver and cleanses the lymphatic system.
10. May improve bone health
Turmeric milk is an excellent source of calcium that is necessary to keep bones healthy and strong.
Indian batting legend Sachin Tendulkar drinks this daily for good bone health.
Turmeric milk slows bone loss and osteoporosis.
11. Benefits of turmeric milk for digestion
It is a powerful antiseptic that promotes intestinal health and treats stomach ulcers and colitis.
This helps improve digestion and prevents ulcers, diarrhea, and indigestion.
12. For menstrual cramps
Turmeric milk works wonders, as it is an antispasmodic that relieves menstrual pain and cramps.
Pregnant women should have golden turmeric milk to facilitate labor, postpartum recovery, improved lactation, and faster contraction of the ovaries.
13. For glowing skin
Cleopatra would bathe in turmeric milk for smooth and supple skin.
Drink turmeric milk for radiant skin.
Dip a cotton ball in turmeric milk and apply it to the affected area for 15 minutes to reduce skin redness and blemishes.
This will make the skin more radiant and glowing than before.
14. Benefits of turmeric milk for weight loss
Are you wondering, benefits of turmeric milk for weight loss?
Well, turmeric milk helps in the breakdown of dietary fat.
This can be helpful in controlling your body weight.
15. Eczema
Drink a glass of turmeric milk every day to treat eczema.
16. Insomnia
Warm turmeric milk produces an amino acid, tryptophan, which induces a peaceful and happy sleep.
17. Benefits of turmeric milk for hair
Treatment Of Scalp
Turmeric milk unravels all your scalp related issues which includes itching, thin hair and swelling as well. It can also crack any fungal infection in the scalp which leads to hair fall.
Cures Hair Fall
Drinking turmeric milk can solve your issue of hair fall as turmeric furnishes all the required nutrition to your hair which leads to strengthening of the hair and reduces the hair fall.
18. Alzheimer’s disease
Good news for all those who have Alzheimer’s! A glass of warm turmeric milk, when taken daily, can help improve your condition by slowing your progress.
19. Benefits of turmeric milk for skin
Trust turmeric milk to give you flawless skin with no side effects.
There is a reason it was seen as a beauty aid in ancient times.
Makes your skin smooth and blemish-free, reduces fine lines, wrinkles, and acne breakouts.
20. Cures autoimmune diseases
Sometimes due to unknown and unexplained reasons, our immune system turns against our own cells and tissues, resulting in autoimmune disorders such as scleroderma, rheumatoid, and psoriasis.
Having a glass of warm turmeric milk is a good way to keep these conditions at bay.
21. Treat headaches
Rely on warm turmeric milk to ease even stubborn headaches.
Turmeric increases the flow of mucus in the system, preventing sinus congestion and preventing sinus problems.
22. Improves reproductive health
As a mild phytoestrogen, turmeric can help promote reproductive health in women.
They are especially recommended for women who cannot conceive due to hormonal imbalances.
How to make turmeric milk
If you want to make turmeric milk for your home, there are a number of simple recipes for a delicious and effective preparation.
Experts agree that you can drink turmeric milk 2-3 times a day, with a maximum of 1 ounce of turmeric (total).
Some of the more popular turmeric milk recipes also include other healthy ingredients, such as almond or coconut milk, but the basic combination of turmeric and milk is also highly effective.
Ingredients
• 1 gram of turmeric
• 1 cup of milk (8 ounces)
• 1/2 teaspoon cardamom powder
• 1/4 teaspoon ginger
Preparation
Step 1 – Heat the milk in a saucepan for 3-4 minutes until lukewarm.
Step 2 – Add the turmeric, cardamom powder, and ginger.
Step 3 – Reduce the heat to medium and let the mixture cook for 1-2 minutes.
Side effects of turmeric milk
Here are some side effects and risk factors associated with turmeric milk, which when ignored can cause serious problems:
• Check for allergies before consuming turmeric milk.
Those who report allergic reactions experience mild, itchy rashes, usually on the neck or face.
• Don’t go overboard with this golden drink.
An overdose can cause heartburn, indigestion, diarrhea, nausea, liver problems, internal bleeding, overactive gallbladder contractions, low blood pressure, alopecia, and menstrual disorders.
• Pregnant women should avoid taking too much turmeric as it can cause contractions of the uterine wall.
• Turmeric can interfere with certain medications, so those taking blood thinners like aspirin should avoid it entirely.
They can also interact with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Consult your doctor before starting to drink turmeric milk.
Now you know what are the best benefits of turmeric milk and why you should consume turmeric milk on a regular basis.
Start reaping the benefits of turmeric with milk today and get clear skin like never before!
Now let’s take a look at some frequently asked questions.
Health
8 shocking health benefits of selenium

Table of Contents
Health
15 shocking health benefits of coriander leaves
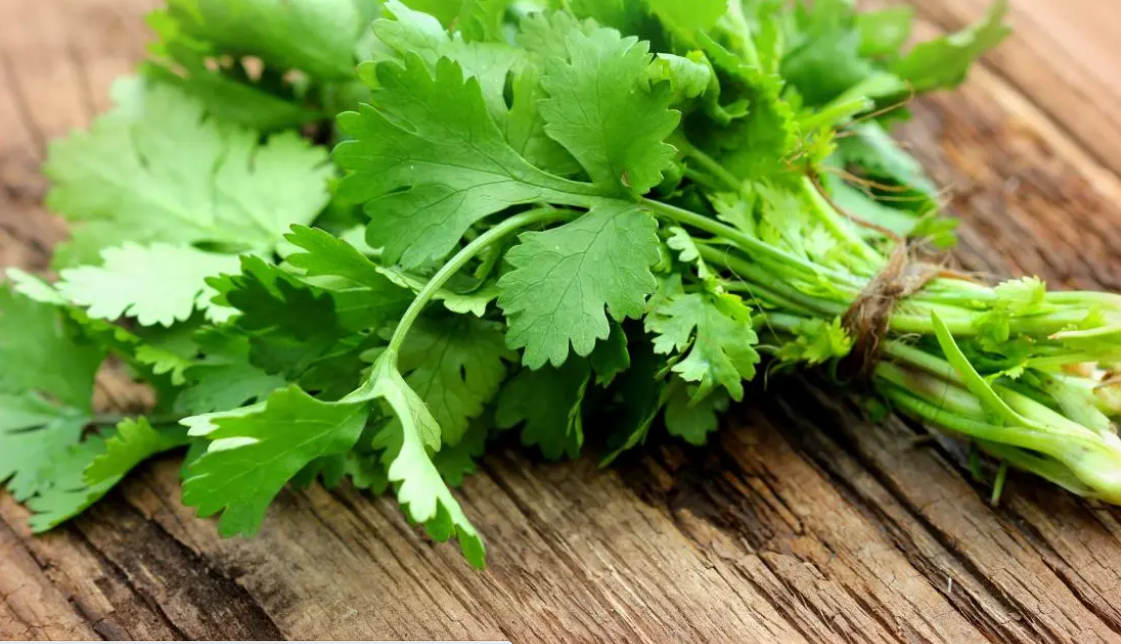

Table of Contents
Discover the 15 shocking health benefits of coriander leaves
There are many health benefits of coriander leaves that you can get which are very helpful as disease prevention and natural treatment method.
Besides, it is very easy to consume these coriander leaves, since you can combine them with other spices when you prepare your food.
Here are several health benefits of coriander leaves that you can get by consuming them in your diet.
1.- Antibiotic
The first health benefits of coriander leaves that you can get are for the antibiotic effect.
Especially when it is used as a treatment for digestive problems, for example, diarrhea that causes pathogens, so they need some antibiotics to cure it.
The reason is that within this plant there are borneol chemicals that can treat various health symptoms such as measles, gastric inflammation, hemorrhoids, flu, vertigo, high blood pressure, vomiting, breast inflammation, and even impotence.
2.- Antioxidant
Many studies are done to show the effectiveness of coriander leaves as an antioxidant.
Among the benefits of coriander leaves, there are antioxidant substances such as chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid, capable of fighting free radicals that cause skin oxidation.
Therefore, if you consume these coriander leaves as part of your daily intake, you will be able to protect your skin from wrinkles due to that free radical.
It turns out that the health benefits of coriander leaves are also usable for cancer.
Especially since there are many types of antioxidants within these leaves that can prevent cancer, such as Vit E, Vit C, caffeic acid, beta carotene, ferulic, kaempferol, and quercetin.
These substances are especially effective in reducing oxidative stress that can cause cancer.
Therefore, if you want to reduce your chances of developing cancer, then you may want to consume coriander leaves regularly.
4.- Inflammation
Among the benefits of coriander leaves, there is one of the most important essential oils is cineole.
Also, within these leaves, there is a component of linoleate acid.
Those two substances are great, especially for protecting you from various problems, like rheumatism and arthritis.
This is also suitable to be used as a treatment for inflammation, especially that which occurs on the skin.
Within these leaves is also atsiri oil, which is especially useful when used against infections caused by bacteria and fungi.
Because there is a lot of substance available within the leaves, it can be used as an antifungal, antiseptic, and disinfectant.
The antioxidant within these leaves is very powerful, so you can even use it to treat eczema and other skin problems.
5.- Heart
The health benefits of coriander leaves are also helpful for those experiencing any problems with their heart condition.
For those who have hypertension, try to consume this because it can lower your blood pressure effectively.
Especially since the calcium and cholinergic ion within these leaves are exceptionally effective in reducing the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, which also includes heart attack and stroke.
The essential oil within these leaves will also make your heart work better.
6.- Diarrhea
Inside the leaves are several essential oils that can make your digestion system work better, such as linalool and borneol. They can make your stomach work better.
Furthermore, you can even use the leaves to cure various digestion system problems such as diarrhea.
The reason is that within the leaves is a helpful substance that can treat diarrhea symptoms such as beta phellandrene, cineole, limonene, borneol, and alpha-pinene.
These substances are known for their antibacterial properties so they can cure the symptoms of diarrhea.
You can also consume coriander leaves when you want to vomit or nausea to relieve symptoms.
7.- Cholesterol
Cholesterol is very bad, as it can cause many types of diseases when not properly treated, such as a heart attack, diabetes, stroke, and many others.
So, if you want to lower the level of available cholesterol in your blood, try consuming these coriander leaves.
The leaves that contain potassium and sodium will be able to reduce them effectively as one of the health benefits of coriander leaves.
Other types of acidic substances that are known to effectively lower the level of available cholesterol within your blood are also available within these leaves, such as linoleate acid, palmitate acid, oleate acid, askorbat acid, as well as stearate acid.
Those substances within the leaves can reduce cholesterol buildup within the vein and artery wall. What’s more,
8.- Iron
These coriander leaves are also known as a good source of iron which is very helpful for many kinds of functions in your body.
First, it is used to make your bone healthy. It is also important in the formation of hemoglobin within your blood, as it will be used to carry oxygen throughout the body.
That is why; If you lack this iron nutrient, your heart beats too fast, you will feel great fatigue and various problems in your respiratory system.
It is also an important nutrient that can prevent anemia from happening to you.
9.- Eyes
As you know, the health benefits of coriander leaves are also very useful for your eyes.
Especially because within these leaves there is a beta carotene substance which is a form of Vit A.
Vitamin A is necessary for your eyes to become healthier and maintain their condition.
Additionally, the antioxidant within the leaves can prevent various eye problems such as cataracts and even macular degeneration.
Health benefits of coriander leaves
10.- Mouth ulcer
Within the leaves, you can also find citronellol, which is a very effective antiseptic.
That is why; you can use it effectively to treat mouth ulcers as it can make the healing process faster and also make your breath feel fresh afterward.
That could be why you may find coriander leaves used as an ingredient in toothpaste.
In the old days, when there was no toothpaste, the leaves were used to eliminate bad breath.
11.- Detoxification
Detoxification is a very important thing because the heavy metal inside your body can cause many kinds of problems in the future, such as autism, dementia, and infertility.
But don’t worry, as the health benefits of coriander leaves can also be used for the detox process.
These sheets are exceptionally effective when used to remove heavy metals that are very dangerous to your body, such as aluminum and even mercury.
12.- Insomnia
There is a time when you can’t sleep even though you don’t really think about anything and aren’t even stressed during the day.
Even though your body is already tired, sometimes you still have trouble sleeping properly.
The reason could be because the chemical composition within your body is an imbalance that makes your body unable to function properly.
This will stiffen your nerves so you will have trouble falling asleep.
When that happens, you may want to try the consumption of coriander leaves, as inside you can find phytonutrients and other substances capable of balancing the chemical composition of the body.
After the chemical composition within your body balances, your nerves will relax and you can easily fall asleep.
13.- Urolithiasis
Other health benefits of coriander leave that you can get come from the natural diuretic properties that this leaf has.
Due to these properties, the consumption of these coriander leaves will be able to promote urine production.
Hence, this sheet is also very effective when used to prevent urolithiasis from occurring.
Also, these leaves that have detoxification properties will detoxify your kidney.
This may reduce the risk of developing kidney stones in the future.
That is why; it is very good for you to consume this coriander regularly.
14.- Diabetes
You should know that by consuming coriander leaves, you will be able to activate your endocrine gland to work.
Furthermore, it will also cause the pancreas to produce more insulin, thereby increasing the level of insulin within the blood.
This insulin will be able to effectively dissolve the sugar in the blood, thus lowering the blood sugar level.
This is an exceptionally important process, especially for you, who have diabetes, so your blood sugar level will decrease by consuming these leaves.
Also, even when you do not have diabetes, consuming coriander leaves may reduce your risk of diabetes.
It can also make your body metabolize sugar better.
Therefore, it is still good for everyone to consume these coriander leaves regularly
15.- Vitamin K
You should know that within these leaves, you can also find vitamin K which has many health benefits from coriander leaves.
If you lack this nutrient, then your body will not be able to process blood clotting because the blood thickening process will be favored with the use of this vitamin K.
Therefore, if you do not get enough vitamin K within your body, then you will keep bleeding every time you get hurt, which will be very dangerous for your life.
Those are several health benefits of coriander leaves that you can get and are exceptionally helpful for treating and even preventing various diseases.
Within these leaves are a large number of essential oils that you can find that also have several useful properties for your health.
You can use these leaves as a natural treatment for various symptoms because the properties these leaves contain are very powerful in treating various diseases.
But it is not only useful as a treatment, this is also useful as prevention of those diseases in the first place.
That is why; The best thing for you is that you can consume these leaves regularly as it is often used as food.
But you should know that some of you might develop allergies after consuming these leaves.
Especially those who often experience allergies to spices so you need to know if you have an allergy when consuming coriander leaves or not.
If you have an allergy, you will also experience irritation to your skin.
So, try taking a little to see the effect before consuming it directly.
Health
16 Benefits of Taurine and side effects

Discover the 16 Benefits of Taurine and side effects.
Taurine is a semi-essential organic compound. Although scientists have known it for more than two centuries; The health benefits of taurine have recently become clear.
A diet rich in taurine can protect the body and promote longevity.
Taurine supplements are non-toxic, cheap, and freely available. Read on to understand why you should consider taurine supplementation and not believe its bad reputation.
Benefits of Taurine
Taurine supplements are recommended for some people, depending on their specific health goals and medical conditions, but it’s important to understand the details of dosage and potential effects.
The most impressive taurine benefits include the following:
•Treatment of Parkinson’s disease
•Improving athletic performance
•Preventing heart disease
•Reducing the risk of diabetes
•Weightloss
•Preventing metabolic syndrome
•Reduce periodontal disease
•Improving muscle growth
1.- Antioxidants
Tissues exposed to oxidative damage have particularly high concentrations of taurine. Like other antioxidants, taurine benefits by directly and indirectly removing harmful oxidants to minimize tissue damage.
Through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, taurine can protect our bodies from unnecessary cell death and tissue damage.
2.- Reduce inflammation
The antioxidant action of taurine benefits produces taurine chloramine (Taul) and bromine (TauBr), which also have anti-inflammatory properties.
Taurine supplementation enhances the formation of TauCl and TauBr in the body and may be effective in treating inflammatory conditions.
Taurine is very effective in treating acute inflammation (caused by infection, irritants, damaged cells, or cancer). However, its role in the progression of inflammatory diseases (such as arthritis) is less clear.
Decreased Taul generation in the body can worsen inflammation-related joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis.
Taul injections improved arthritis symptoms in various experimental animal models.
The gene for the taurine transporter (TauT) has also been linked to the inflammatory response.
3.- Fight infections
The antimicrobial effects of taurine benefits in the body come from taurine chloramine (Taul) and taurine bromine (TauBr) formation.
Taul and TauBr are capable of killing a wide spectrum of bacteria, fungi (yeasts and molds), viruses, and parasites.
Both Taul and TauBr are promising treatments for infections such as chronic sinusitis, otitis media (swimmer’s ear), acne vulgaris, and gum disease.
Taul and TauBr break down quickly in our bodies and are only effective if used topically, not supplemented. However, taurine supplementation can increase the production of these compounds in our bodies.
Taurine’s role as an antioxidant is also important for the protection of the cells of our immune system.
Taurolidine, another taurine derivative, is commonly used in Europe and the US to help treat various infections.
The white blood cells (neutrophils) of rats supplemented with taurine have an increased ability to destroy invading bacteria.
4.-Help fight cancer
Taurolidine, a taurine derivative that is converted to taurine within the body, increased cancer survival rates in animal models; it also blocked the growth of colorectal cancer in rats.
Cancer patients have reduced levels of taurine. Surgery and chemotherapy further lower taurine levels and can reduce taurine in cancer patients. Therefore, taurine supplementation can be very beneficial for cancer patients.
5.-Treat diabetes
Antioxidants, such as taurine, are low in diabetic individuals. This increases the risk of oxidative damage; diabetes decreases the body’s ability to absorb taurine.
Diabetic complications, such as heart, kidney, and nerve damage, can be attributed to high oxidative damage as a result of low taurine levels.
In a study of 39 types 1 diabetic patient, oral supplementation with 500 mg of taurine three times daily for 3 months restored blood taurine levels. Taurine supplementation also prevented blood cells from clotting, lowering the risk of a heart attack.
In rats, taurine also lowers blood glucose by interacting with insulin receptors on cells.
The role of taurine benefits in protecting the kidneys from damage in diabetes is well documented in animal models and human cells.
One and a half grams of taurine daily for two weeks improved early cardiac abnormalities in a study (DB-RCT) of nine types of diabetic patients.
6.-Protects the heart
Cells of the heart and blood vessels contain the taurine transporter, suggesting that the benefits of taurine are important for heart function.
Heart disease induced by taurine-deficient diet in various animal studies.
The risk of chronic heart disease is lower in individuals with a high urinary production of taurine.
In a study of 22 healthy middle-aged women, 3 g of taurine supplements daily for 4 weeks lowered homocysteine levels. Since homocysteine correlates with heart disease, taurine may help prevent heart attacks or high cholesterol.
Taurine can also prevent abnormal heartbeats (AFib)
Taurine supplementation is effective in treating the hardening and narrowing of blood arteries in animals.
Although more research is needed, the positive effects of taurine’s benefits on the heart are thought to:
•Improves fat profile
•Helps control calcium ion uptake and thus cell excitation
•Acts as an antioxidant
•Prevents contraction of blood vessels
7.- Prevents hypertension
Taurine can increase the production of endorphins by the brain (hypothalamus). This calms the brain’s fight or flight response, which is overactive during stress, and lowers blood pressure.
Low levels of taurine are associated with increased blood pressure.
Oral taurine supplementation is potentially a very safe and convenient regimen for the control of high blood pressure.
Consumption of 3g of taurine per day for 2 months in hypertensive patients reduced both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
It also plays a protective role in the heart and kidneys in rats with hypertension.
8.- Reduces cholesterol
Taurine supplementation can improve bile secretion and activity and improve the body’s breakdown of cholesterol.
It is also essential for the formation of bile salts and as such plays an important role in the absorption and breakdown of fats and cholesterol.
Additionally, taurine can lower blood and liver cholesterol levels in animals fed a high-fat diet.
9.-Protects the liver
Taurine supplementation in the diet at doses greater than 500 mg daily for 3 months reduced liver injury in 24 patients with chronic hepatitis.
In rats, dietary taurine protected their livers from damage related to heavy metals and oxidized fat.
Taurine availability in the body is low in various forms of liver cirrhosis. In 35 patients with liver cirrhosis, daily taurine supplementation increased taurine levels and also reduced painful muscle cramps that are associated with cirrhosis.
In animal models, taurine is effective in preventing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. It reduced oxidative stress, cell death, and fat accumulation in the liver.
Taurine supplementation also prevented alcoholic fatty liver disease in animals by decreasing alcohol-induced oxidative stress and inflammation. It also increased the production of proteins associated with the breakdown of fats in the liver.
Animal studies suggest that taurine prevents long-term liver damage and helps liver cells recover more quickly from fatty and alcoholic liver disease.
10.- Parkinson’s disease
Research has shown that when people have adequate or high levels of taurine in their system, neuronal cell regrowth is possible, which may help reverse or mitigate the effects of certain neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease.
11.- Weight loss
Lowering fat levels in the bloodstream and helping the body deal with excess blood glucose are two of the best benefits of taurine; therefore, they can help optimize the process of weight loss and fat burning.
12.- Athletic performance
This organic compound has become a very popular training supplement as it is known to allow muscles to work longer, safer, and more efficiently, which means your workouts will have better results and your recovery time will be faster. shorter.
13.- Immune function
Having adequate levels of taurine in your body can help your immune system regulate its actions, meaning your body is less likely to experience allergic reactions and other unnecessary energy expenditure.
14.- Muscle development
Taurine benefits are known to aid in skeletal muscle differentiation, and later in life, having adequate levels can help you grow and strengthen your muscles more effectively, making it a popular additive for bodybuilders and powerlifters. dumbbells.
15.- Protects vision
Taurine benefits protect retinal cells from damage caused by oxidants and bright light; In a study (DB-CT) of 62 patients, a combination of taurine, diltiazem, and vitamin E helped decrease vision loss by protecting against oxidative damage.
Low levels of taurine are associated with cataract formation in humans.
In cats, taurine deprivation causes vision loss.
In rats, the antiepileptic drug Vigabatrin depletes retinal taurine. As a result, prolonged use of this drug can lead to irreversible vision loss.
16.- It is good for lung health
The antioxidant activity benefits of taurine can protect the lungs from damage caused by exposure to toxins such as cigarette smoke.
Taurine-fed hamsters can resist lung damage caused by exposure to air pollutants.
Maintenance of tissue taurine levels is critical for the prevention of oxidant-induced lung injury in rats.
In sheep, the taurine-derived taurolidine (which is converted to taurine in the body) prevents lung damage caused by bacterial toxins.
Frequently asked questions about the benefits of taurine
-What is taurine?
Taurine (L-taurine or 2-aminoethane sulfonic acid) is a sulfur-containing amino acid.
Mammals have taurine in almost all tissues, but the heart, brain, retina, platelets, and glands contain particularly high amounts.
Taurine plays a crucial role in the development and protection of cells within mammals; controls multiple important biological processes in the body.
In this sense, taurine could be more easily compared to sodium or calcium ions than to a drug that targets a specific receptor in our body.
Humans are capable of producing taurine, but not in sufficient quantities. Therefore, taurine is a conditionally essential amino acid for humans; Some conditions in which patients may be deficient in taurine include premature infants, newborns, and patients with chronic liver, heart, and kidney disease.
This supplement is also an osmolyte. This means that it controls the entry and exit of water in the cells and prevents them from changing the cell too much; It interacts with fats in cell membranes and stabilizes them, preventing structural changes in the cell.
Despite the impressive range of positive effects that taurine has on the body, its exact mechanisms of action remain largely unknown.
-How does the body produce taurine?
Taurine is synthesized in the body from the only other two sulfur-containing amino acids, methionine and cysteine.
Taurine synthesis occurs primarily in the liver, with the help of the enzyme cysteine sulfinic acid and vitamin B6 (pyridoxine).
Other cells in our body can absorb taurine from the blood thanks to the special taurine transporter molecule (TauT) found in cell membranes.
Taurine is an essential nutrient for newborns as they are not yet able to synthesize or retain taurine within their bodies. Breast milk contains the full taurine requirement for infants, as does modern infant formula.
-How does the body eliminate taurine?
Taurine leaves the body as part of the bile or urine.
The kidneys can increase or decrease taurine excretion depending on the dietary availability of taurine. High amounts of taurine in urine indicate high dietary intake.
Taurine carrier molecules in the kidneys use energy to reabsorb and retain taurine in the body.
People with compromised kidney function or defective taurine transporters may not be able to retain sufficient amounts of taurine.
Taurine Side Effects
Taurine remains one of the most important organic compounds within the body, but there are some potential side effects when consuming too much, such as pregnancy complications and worsening of certain nervous system disorders.
Bipolar Disorder: Studies have found that regular or prolonged use of this compound can worsen the symptoms of bipolar disorder, although, in moderate amounts, it may have a mitigating effect on this condition.
Pregnancy: Some of the more popular taurine supplements also contain other active ingredients, including caffeine, that may pose a risk to pregnant or lactating women, so these individuals should avoid the use of this non-essential amino acid.
Dosage
Up to 3 g of supplemental taurine per day is safe for consumption in adults. There is strong evidence that there are no side effects at doses up to and below this value. Scientists do not recommend a dose greater than 3 g per day.
Relatively high amounts of taurine are safe for consumption because any excess can be passed harmlessly through urine.
-

 Benefits4 months ago
Benefits4 months agoThe Benefits of Joining Gym Lumolog – Improve Your Fitness & Health
-

 Food1 year ago
Food1 year ago10 + Benefits of carrot juice and side effects
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year ago50 Super Healthy (And Very Often Cheap) Foods
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year ago5 Shocking health benefits of kinkeliba and side effects
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year ago15 health benefits of soursop leaves tea and side effects
-

 Food1 year ago
Food1 year ago8 shocking benefits of leek juice and side effects
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year ago15 Benefits of lipton tea and side effects
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year agoBenefits of guava leaves Sensually