Health
Cinnamon and diabetes: how to use it to lower your blood sugar level

Discover how to use Cinnamon for diabetes.
Why and how to use cinnamon to lower the level of sugar and fat in the blood?
Cinnamon, also known as “poor man’s insulin”, has long been known for its action on diabetes and cholesterol. Let’s see here why it is advisable to consume cinnamon when you have diabetes, and how to take cinnamon for an effective effect.
Be aware, however, that under no circumstances should you stop taking the medications prescribed by your doctor, and take advice from him if you want to take cinnamon.
This way to buy cinnamon, the aromatic bark of the cinnamon tree used in cooking and therefore as a natural remedy against diabetes.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is chronic hyperglycemia, an excess of sugar in the blood causing blood sugar that is too high compared to the average. This excess of sugar is the consequence of poor assimilation, poor use and poor storage of sugars by the body.
Indeed, in a normal organism, the carbohydrates in the diet are transformed into glucose, the pancreas then detects the increase in blood sugar and will produce insulin.
This insulin helps glucose to enter body cells (muscles, organs, etc.) and the liver where it will be processed and stored. Blood sugar levels then decrease in the blood.
For people with diabetes, this regulatory system does not work and must be supported by injections of insulin through injections.
There are mainly two types of diabetes :
- Type 1 diabetes: or insulin-dependent diabetes, about 6% of diabetics. It is characterized by insufficient production of insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes: or non-insulin-dependent diabetes, 92% of diabetics. It is characterized by initially an insulin resistance of certain organs which prevent the entry of insulin.
This resistance to the action of insulin leads to an overproduction of insulin by the pancreas to compensate, a pancreas which gets tired and after twenty years, no longer produces enough insulin: this is the insulin deficiency.
You should know that this type of diabetes increases the risk of cardiovascular disease by 2 to 4 times (heart attack, high blood pressure, etc.).
Can cinnamon lower your blood sugar
A simple answer would be: yes! But let’s dig into the subject a bit.
To go further, find out what are the virtues of cinnamon.
For the little story :
It is a happy mistake that led Western researchers to find the effect of cinnamon on blood sugar (although this effect has been known for ages in Asia).
Indeed, we owe this discovery to Dr Richard A. Anderson, who originally studied the properties of chromium. USDA researcher, senior scientist at Beltsville Human Nutrition Research Center, Beltsville, and physician.
He has published over 230 scientific manuscripts and presented over 200 presentations at regional, national and international meetings around the world.
While studying the effects of chromium on diabetes, he realizes that apple pie stimulates insulin activity. No sense, the apple pie contains only a little chromium and a lot of sugar!
Anderson then thinks of the effect of apples, but quickly realizes that this effect is due to another ingredient in the pie… cinnamon!
The scientist will therefore focus his studies on the effects of cinnamon on diabetics. Many other scientists will follow, all convinced that cinnamon is the best hope for a natural cure for diabetes.
What evidence for the effect of cinnamon on diabetes?
Following Dr Anderson’s discovery, hundreds of studies are being conducted on the bark by hundreds of scientists. Finally, it is Dr Anderson who will publish in 2010, a scientific article taking stock of the 16 main studies on cinnamon.
Of these 16 studies, 11 show a significant effect of the spice, and 5 show little or no influence on the drop in blood sugar.
CASES WHERE CINNAMON HAS LITTLE OR NO EFFECT:
Regarding these latest inconclusive or inconclusive studies, patients were taking metformin, one of the most common treatments for type 2 diabetes.
According to Anderson: “Metformin acts like cinnamon, increasing insulin sensitivity. If you take enough metformin to manage blood sugar, cinnamon will not affect”.
The poor or inconclusive studies have shown no effect on young people with type 1 diabetes, a logical result, because people with type 1 diabetes have little or no insulin, and cinnamon is not a substitute for it. insulin.
A study has shown that cinnamon does not lower blood sugar levels in healthy people without any diabetes problem.
There are still studies, conducted on other patients that have not led to conclusive results.
CASES WHERE CINNAMON HAS A SIGNIFICANT EFFECT:
The most significant study was conducted by Dr Anderson with a team of researchers from the Peshawar School of Agriculture.
This study was carried out on 60 middle-aged patients suffering from type 2 diabetes, divided into 6 groups. Group 1 took 2 capsules of cinnamon per day, group 2 took 6 and group 3 took 12. The other groups had the same amounts of capsules, but a placebo.
Treatment was carried out for 40 days in all groups, and the capsules contained 500 mg of cinnamon (approximately 1/4 teaspoon). The patients ate as usual while taking their diabetes medication, but not metformin.
The result: in the groups taking cinnamon, there was a drop in blood sugar levels of 18 to 29%. We also observed a drop in triglycerides from 23 to 30%, in total cholesterol from 13 to 26%, and bad cholesterol (LDL cholesterol) from 10 to 24%.
A study conducted by researchers at the University of Pomona in California (USA) on 543 patients with type 2 diabetes arrived at the same conclusions, showing besides that cinnamon increases the level of good cholesterol (HDL).
How does cinnamon affect blood sugar
The magic compound that comes into play is called: polymer methylhydroxychalcone (MHCP), the most active compound in the bark.
Indeed, studies by Professor Anderson have shown that this substance increases the metabolism of glucose up to 20 times, the process which converts sugar into energy. As such, cinnamon is the ally of diets!
Cinnamon facilitates the work of insulin and therefore helps to get sugar into cells. As such, it would affect comparable to certain drugs such as thiazolidinediones (Actos®, Avandia®, etc.), which reduce insulin resistance.
Also, MHCP is a formidable antioxidant, from a class of polyphenols found in cocoa beans, which also has an impact on diabetes.
Antioxidants prevent the formation of free radicals, which damage the DNA of cells and which therefore lead to chronic diseases, including diabetes. There are many studies on the action of antioxidants on diabetes and cholesterol reduction.
What variety of cinnamon for diabetes?
As I explain in our article on how to lose weight with cinnamon, there are two varieties, which come from the bark of two very similar but different tree species:
- Cinnamomum Verum, known as Ceylon cinnamon, also known as real cinnamon,
- Cinnamomum aromaticum or Cinnamomum cassia, known as cinnamon from Indonesia or China, also known as false cinnamon.
Let’s be clear: when it comes to lowering blood sugar and cholesterol, variety doesn’t matter, they have the same effect. That said, for long term use, we still recommend Ceylon cinnamon.
Indeed, their health benefits are the same, with one exception that makes all the difference: coumarin. It is the coumarin concentration that differs in the two species.
Ceylon cinnamon bark (Cinnamomum Verum) hardly contains any, but on the other hand, Chinese cinnamon bark (Cinnamomum cassia) is rich in it.
Except that coumarin is potentially toxic to the liver because it has hepatotoxic properties. So for long term consumption, prefer Ceylon cinnamon.
How to take cinnamon?
The different ways to do it:
It should be consumed daily, whatever the way. We recommend doses between 1 and 4 g (between 1/2 and 1 teaspoon per day) of Ceylon cinnamon per day, even if studies have not made it possible to update an ideal dosage. You can consume it:
- For breakfast: in cottage cheese, on your cereals, on a fruit salad, etc.
- In your savoury dishes: yes, especially in the Maghreb and in the East, it is found in salty dishes: couscous, tagines, etc.
- In the preparation of your desserts: to add directly to your preparations.
- Like a drink: in milk ( recipe for cinnamon milk ), in your tea, fruit juice (apple, orange, grape, etc.), smoothies, etc.
You can also just make an infusion of cinnamon, by boiling a cup of water, then infusing a few cinnamon sticks, or a teaspoon of ground cinnamon, covered, for 10 min.
Do not hesitate to sweeten with honey, the benefits of both are very beneficial, discover, on this subject, our article on the virtues of honey with cinnamon.
Cinnamon has a sweet flavour that will replace sugar in all your preparations.
Does cinnamon work quickly?
The first effects on blood sugar are felt after 2 weeks of daily absorption.
The first effects on cholesterol and triglycerides may take months to appear.
Contraindication and side effects:
The consumption of cinnamon is not without risk, we have devoted an article detailing the possible problems associated with the consumption of cinnamon, where you will find the contraindications, drug interactions, side effects, etc.
If using Indonesian cinnamon (Cinnamomum cassia), do not exceed 1/2 teaspoon per day. The coumarin present in this variety is an anticoagulant, be careful if you are on anticoagulant treatment.
Rarer, coumarin, in large amounts and over long term consumption can cause liver damage.
Excessive consumption of cinnamon can cause side effects: increased heart rate increased blood pressure and palpitations.
To sum up “cinnamon and diabetes”:
Should we consult a doctor? Yes, yes, and again yes, never stop treatment and seek the advice of your doctor before embarking on any cure.
Is it effective? Yes, but not for everyone.
For who? People with prediabetes, metabolic syndrome or type 2 diabetes, if you are not taking metformin. It is possible to consult your doctor to see if it is possible to lower the doses of metformin by adding cinnamon to your diet.
How? ‘Or’ What? Add cinnamon (preferably Ceylon) every day to a healthy diet and exercise for 20 minutes per day.
Health
7 Benefits of jujube seeds and side effects

Table of Contents
Health
Benefits of coconut water in pregnancy

Discover the benefits of coconut water in pregnancy.
Coconut water is a clear, sweet, energizing isotonic drink that helps your body replenish lost fluids. Also known as Nariyal Pani and Elaneer in India, it is known for its versatility and countless nutritional benefits.
IS IT SAFE TO CONSUME COCONUT WATER DURING PREGNANCY?
Yes, it is safe to drink coconut water, but in moderation, as it contains natural vitamins and minerals.
Having coconut water in the first trimester helps curb dehydration resulting from morning sickness. It’s also good for heartburn and constipation, common symptoms of pregnancy.
You can drink coconut water at any time, but the best time is early in the morning. It is healthier, as the electrolytes and nutrients can be easily absorbed when the stomach is empty.
The nutritional benefits present in a cup of coconut water include:
•Calories 46
•Sodium 252mg
•600mg potassium
•Carbs 8.9 grams
•Dietary fiber 2.6 grams
•Sugars 6.26 grams
•Calcium 6%
Benefits of coconut water in pregnancy
You can reap its benefits only when you consume fresh water, as it begins to ferment when left open and exposed to air.
1. NATURAL DIURETIC:
During pregnancy, uric acid levels should be normal in your body system. Coconut water is a diuretic and increases the need to urinate due to the presence of potassium, magnesium, and minerals.
They help eliminate toxins and cleanse the urinary tract. Thus, it improves kidney function and prevents kidney stones and infections. It also prevents urinary tract infections, which reduces the chances of preterm labor.
2. OFFERS ESSENTIAL ELECTROLYTES:
The need for electrolytes increases during pregnancy because conditions like morning sickness, nausea, and diarrhea dehydrate the body. Coconut water supplies all five essential electrolytes: minerals, sodium, calcium, potassium, and phosphorus, which calm the body and provide energy.
These electrolytes transmit electrical charges in your body and aid in muscle function. They also help maintain your body’s pH levels and control blood pressure levels. It is known to have cooling properties, which prevent conditions such as bilious fever and vomiting.
3. RELIEVES HEARTBURN AND CONSTIPATION:
Hormonal changes during pregnancy lead to various problems like heartburn, constipation, and indigestion. The rich content of dietary fiber in coconut water strengthens the digestive system, improves digestion, regulates pH levels, and prevents constipation.
Ayurveda considers young coconut water to be an excellent laxative. Improves metabolism and detoxifies the body. Coconut water is a natural acid neutralizer and thus prevents heartburn.
4. TREAT INFECTIONS:
Coconut water is rich in vitamins, essential minerals, and antioxidants, which boost your immune levels, providing resistance to infections. It contains lauric acid, a medium-chain fatty acid responsible for the production of a powerful antiviral monolaurin, Michelle-Lee Young writes in the book “Two Trees and Twelve Fruits That Will Change Your Life Forever.” Lauric is a disease-fighting acid that kills harmful bacteria and infections like the flu, and HIV, and retains good bacteria.
5. IMPROVES HEART HEALTH:
Low electrolyte level increases blood pressure. Drinking coconut water improves levels of potassium, magnesium, and lauric acid, which help regulate blood pressure. Improves good cholesterol and fights bad cholesterol.
The vitamins, essential proteins, and electrolytes in coconut water control sugar levels, and blood pressure levels, and improve circulation. A glass of coconut water every day is particularly helpful in the last trimester when there is increasing stress from labor that can increase your blood pressure.
6. MAINTAINS A HEALTHY WEIGHT:
Coconut water is fat-free and low in calories. As pregnancy adds extra weight to your body, coconut water prevents fat accumulation by removing bad cholesterol. It is an excellent replacement for sugary drinks and helps both the mother and the growing fetus to be healthy and fit.
7. NATURAL DRINK:
Coconut water is a tasty natural drink. It has no artificial flavors or harmful components. It is safe for you and your growing fetus as none of its components affect your health.
8. ENERGIZE AFTER TRAINING:
Coconut water is a natural isotonic drink, which helps you gain energy when suffering from dehydration, fatigue, and exhaustion. It is a great revitalizer
. If you exercise regularly to stay fit and strengthen your pelvic muscles, you can opt for coconut water as an energy drink. Hydration also improves skin elasticity, limiting the stretch marks that develop during pregnancy.
9. LOW SUGAR CONTENT:
Excessive sugar intake can lead to an increase in overall blood sugar levels. Coconut water has less sugar than other sports and energy drinks. You won’t gain pregnancy weight, and a diet low in simple sugars will reduce your risk of getting gestational diabetes.
10. ACCELERATES THE GROWTH OF THE FETUS:
Coconut water offers all the nutrients to the mother, essential to maintain and improve her health. Thus, it improves the health, growth, and proper nutrition of the unborn baby.
11. IMPROVES AMNIOTIC FLUID LEVELS:
Drinking coconut water improves the overall health and environment of your growing fetus. Coconut water taken especially in the third trimester increases amniotic fluid levels and improves blood volume and circulation.
ARE THERE ANY SIDE EFFECTS OF COCONUT WATER DURING PREGNANCY?
There is no evidence that coconut water has adverse effects on pregnancy. Like any other fruit or vegetable juice, it also appears to be safe. But there are two things to keep in mind:
•Coconut milk contains sodium, which may not be the right choice for pregnant women with preeclampsia.
•Ripe coconut water can cause constipation.
HOW MUCH COCONUT WATER CAN A PREGNANT WOMAN HAVE?
Moderation is always the key when it comes to eating a healthy diet. You can drink up to a glass of coconut water a day.
Consume the water soon after opening, as a fresh one will contain rich nutrients. Use a clean straw or pour it into a glass and drink.
It is always good to prefer natural coconut water to canned or bottled.
Do not consume coconut water if you react or do not like its taste.
HOW TO SELECT THE CORRECT COCONUT?
To enjoy the various benefits of coconut water, you need to know how to select them properly. These tips can help you buy fresh and tender coconut.
A fresh coconut will be light and sweet and will not contain coconut meat, the white, meaty, tender substance. A ripe or stale one will taste sour.
Selection: Choose medium-sized, clean, green walnuts, as they contain large amounts of water. Don’t choose coconuts that have hard brown shells and gray patches as they indicate ripe nuts.
Water: Shake the coconut vigorously near your ear to check for water. Select the ones that make a good splashing sound. A fresh coconut will contain almost a cup of water.
If you want to store coconuts at home, keep them in a cool place.
BENEFITS OF COCONUT MEAT DURING PREGNANCY:
1. GENERATION OF BREAST MILK:
Regular consumption of coconut meat during pregnancy improves the supply of breast milk after childbirth. Your baby will receive nutritious and rich breast milk. Also, coconut oil helps in the generation of breast milk.
It is also good during the lactation phase as it contains lauric and capric acids. These acids have antiviral, antibacterial, and parasiticidal effects, which protect the baby from diseases.
2. IMPROVES BLOOD CIRCULATION:
Blood volume doubles during pregnancy, causing swelling of the feet and legs. Poor blood circulation aggravates the condition. Coconut consumption improves blood circulation and prevents swelling and pain in the legs.
3. HELPS DIGESTION:
Consuming coconut meat and water prevents constipation as tender coconut meat acts as an excellent laxative. It is one of the best benefits of consuming a coconut in any form during pregnancy.
4. BETTER SLEEP:
Having coconut in combination with poppy seeds and ghee will improve your sleep cycle.
5. INCREASES METABOLISM:
When the coconut is mixed with spices, it helps boost metabolic activities in pregnant women.
COCONUT MILK DURING PREGNANCY:
Coconut milk is a thick, milky liquid obtained by grinding grated coconut meat. It is also an essential ingredient in many foods, especially Southeast Asian dishes.
Coconut can be consumed in any form due to its amazing health benefits. Coconut milk helps increase body fuel. It is completely safe to drink unless you are allergic to it.
BENEFITS OF COCONUT MILK DURING PREGNANCY:
1. ENHANCE IMMUNITY:
Coconut milk contains lauric acid, which is an antibacterial and antiviral fat, useful for pregnant women. This type of fat helps improve the immune system, according to the book “Coconut Oil and the Immune System” by Sherri Neal. The long-chain fatty acids straighten the blood vessels and reduce any blockages in the heart, thus improving the condition of the heart as well.
2. OTHER BENEFITS INCLUDE:
•It contains good amounts of iron, which can treat anemia.
•Improves digestive problems.
•It offers relaxation to the muscles and the nervous system.
•Controls blood sugar levels and blood pressure
•Relieves joint pain and scratches
•Makes your body fit and helps you lose weight
HOW TO PREPARE FRESH COCONUT MILK?
It is advisable to make coconut milk at home instead of opting for a packaged one.
Grate a whole coconut and add a cup and a half of hot water.
Let the mixture cool to room temperature.
Once the mixture cools down, strain to get the milk.
Coconut milk taken directly from fresh coconuts will contain approximately 450 calories and 50 g of fat. A cup of coconut milk (approximately 240 g) has the following nutritional values:
•Calories 550
•Fats 50.2gm (all types of fats)
•Cholesterol 0
•Sodium 40gm
•Carbohydrates 14gm (in 250gm of milk)
•Proteins 6gm
•Vitamin C 11%
•Iron 22%
•Calcium 4%
IS CANNED COCONUT MILK GOOD DURING PREGNANCY?
It’s safe to have canned coconut milk during pregnancy, but you need to make sure the can isn’t corroded, rusted, expired, or stored at dangerous temperatures.
Coconut milk contains considerable amounts of saturated fat, that is, 3 g in a tablespoon. Eating too much-saturated fat will increase the levels of good and bad cholesterol in the body. In the case of canned milk, you must take into account your level of consumption, since you should not exceed your daily requirement.
In addition to the above, other reasons why you may not choose canned coconut milk are:
1. BISPHENOL A (BPA):
It is a chemical that is typically used in the lining of cans used for packaged foods. This BPA can gradually leach into acidic, fatty, or salty foods like coconut milk, vegetables, tomatoes, and soups. One study claims that there is a relationship between high levels of BPA in mothers and neurobehavioral problems in babies.
2. GUAR GUM:
Guar gum is an additive present in canned coconut milk. It is a galactomannan, a polysaccharide, and is primarily a ground endosperm of guar beans.
There have been complaints such as severe abdominal cramps, indigestion, flatulence, and diarrhea, as beans are difficult to digest. In a clinical experiment, patients with intestinal problems showed improvement when they stopped using canned coconut milk in their diet.
3. FRUCTOSE MALABSORPTION:
It is a digestive disease characterized by impaired transport of fructose (a simple sugar found in fruits, vegetables, and honey) through the small intestine. Increased fructose levels in the gut cause bacterial overgrowth.
Therefore, it reduces the absorption of water in the intestine. Pregnant women with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) are highly affected by fructose malabsorption.
According to nutrition data, coconut milk contains sugar, including fructose. Therefore, it should be avoided by those affected by IBD and IBS disorders.
Health
Disadvantages of miscegenation reproduction
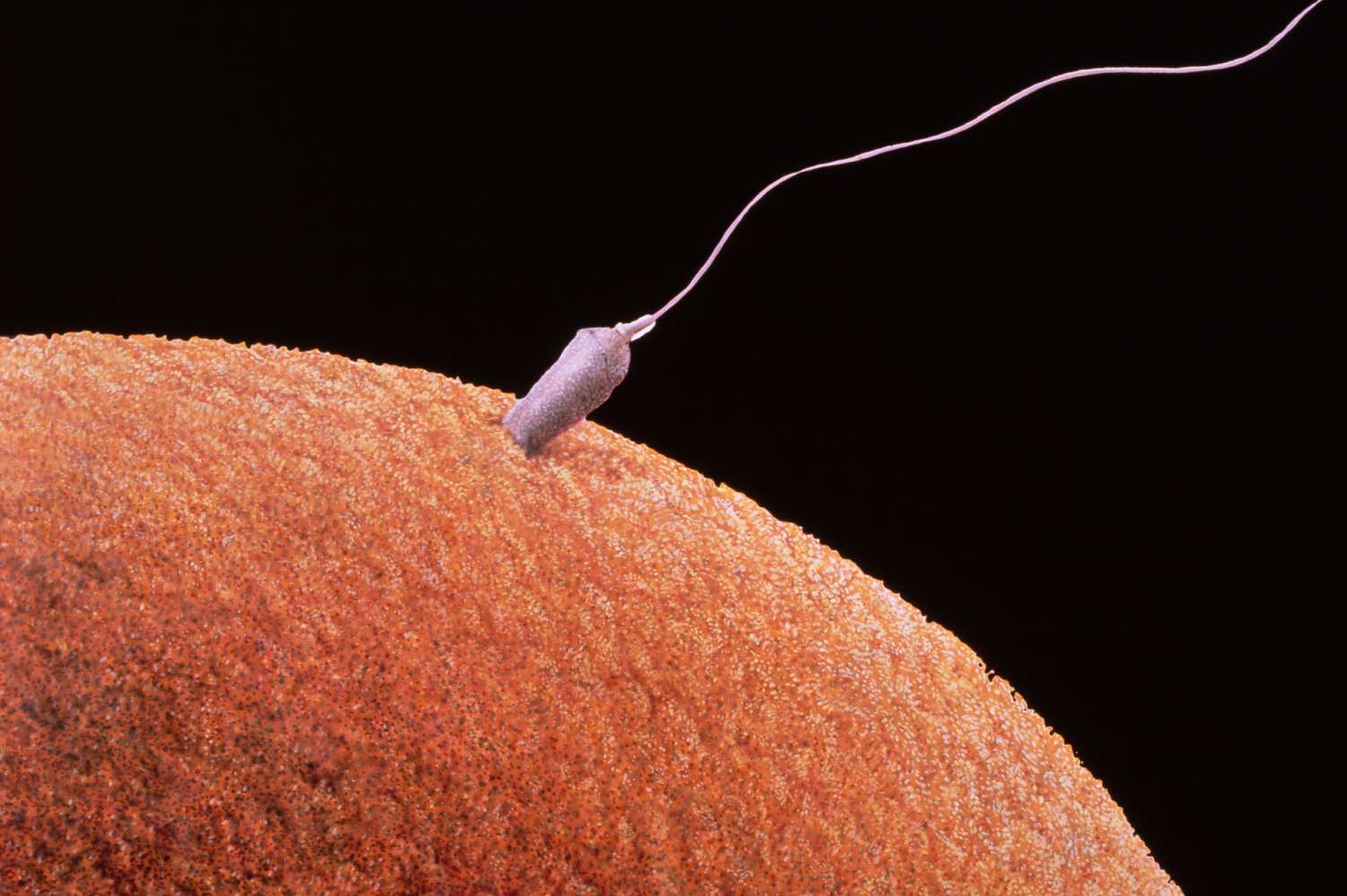
Table of Contents
-

 Food1 year ago
Food1 year ago10 + Benefits of carrot juice and side effects
-

 Benefits4 months ago
Benefits4 months agoThe Benefits of Joining Gym Lumolog – Improve Your Fitness & Health
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year ago50 Super Healthy (And Very Often Cheap) Foods
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year ago5 Shocking health benefits of kinkeliba and side effects
-

 Food1 year ago
Food1 year ago8 shocking benefits of leek juice and side effects
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year agoBenefits of guava leaves Sensually
-

 Weight Loss1 year ago
Weight Loss1 year agoChaz Bono weight loss secret
-

 Health1 year ago
Health1 year ago13 shocking health benefits of Thai eggplant












